Length-Dependent Formation of Transmembrane Pores by 310-Helical α-Aminoisobutyric Acid Foldamers
10.1021/jacs.5b12057
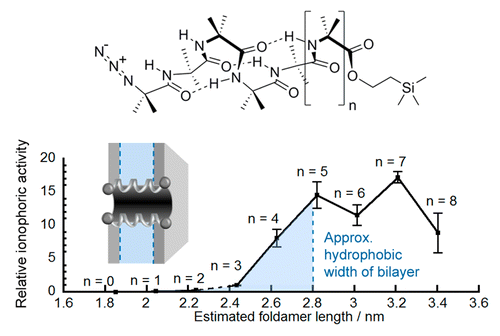
Foldamer designs to match membrane thickness.
The synthetic biology toolbox lacks extendable and conformationally controllable yet easy-to-synthesize building blocks that are long enough to span membranes. To meet this need, an iterative synthesis of α-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) oligomers was used to create a library of homologous rigid-rod 310-helical foldamers, which have incrementally increasing lengths and functionalizable N- and C-termini. This library was used to probe the inter-relationship of foldamer length, self-association strength, and ionophoric ability, which is poorly understood. Although foldamer self-association in nonpolar chloroform increased with length, with a ∼14-fold increase in dimerization constant from Aib6 to Aib11, ionophoric activity in bilayers showed a stronger length dependence, with the observed rate constant for Aib11 ∼70-fold greater than that of Aib6. The strongest ionophoric activity was observed for foldamers with >10 Aib residues, which have end-to-end distances greater than the hydrophobic width of the bilayers used (∼2.8 nm); X-ray crystallography showed that Aib11 is 2.93 nm long. These studies suggest that being long enough to span the membrane is more important for good ionophoric activity than strong self-association in the bilayer. Planar bilayer conductance measurements showed that Aib11 and Aib13, but not Aib7, could form pores. This pore-forming behavior is strong evidence that Aibm (m ≥ 10) building blocks can span bilayers.